Online chess textbook: Rules of chess. How to learn to play chess from scratch on your own and reach the level of a pro? How to play chess alone
Our step-by-step instruction help you learn the game of chess easily.
It's never too late to learn how to play chess - the most popular game in the world! Learning the rules of chess is easy:
Step 1. How to install the board
Before the game, the board is positioned so that in the lower right corner in front of each player there is a white field.

Step 2. How the pieces move
Each of the 6 pieces moves differently. Pieces cannot jump over other pieces (with the exception of the knight) or enter a square where a piece of the same color is already standing. However, they can take the place of an opponent's piece, which is considered captured. Pieces are usually placed to threaten opponent's pieces with a capture (to stand on the square where the captured piece stood, replacing it), to defend their own pieces that are threatened with a capture, or to control important squares on the board.
How to move the king in chess
The king is the most important piece, but also one of the weakest. The king can only move one square in any direction: up, down, sideways and diagonally. The king can never stand on an attacked square (where an opponent's piece can take it). When the king is attacked by another piece, it is called "check".

How to move the queen in chess
The queen is the strongest piece. It can move in a straight line in any direction - forward, backward, sideways, or diagonally across any number of squares - but it cannot jump over other pieces. If the queen or any other piece captures the opponent's piece, the turn ends. Watch as the white queen captures the black one, forcing the black king to move.

How to move the rook in chess
The rook can move any number of squares, but only forward, backward and sideways (not diagonally). Rooks are especially strong when they protect each other and work together!
How to move the bishop in chess
The elephant can move in a straight line to any number of squares, but only diagonally. During the game, each bishop always moves to squares of the same color (white or black). Elephants work well together as they cover each other's weaknesses.
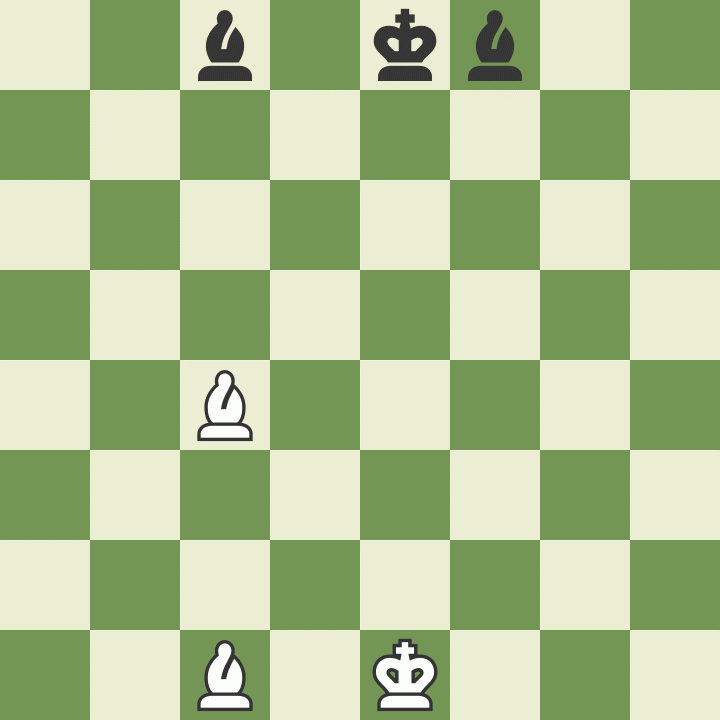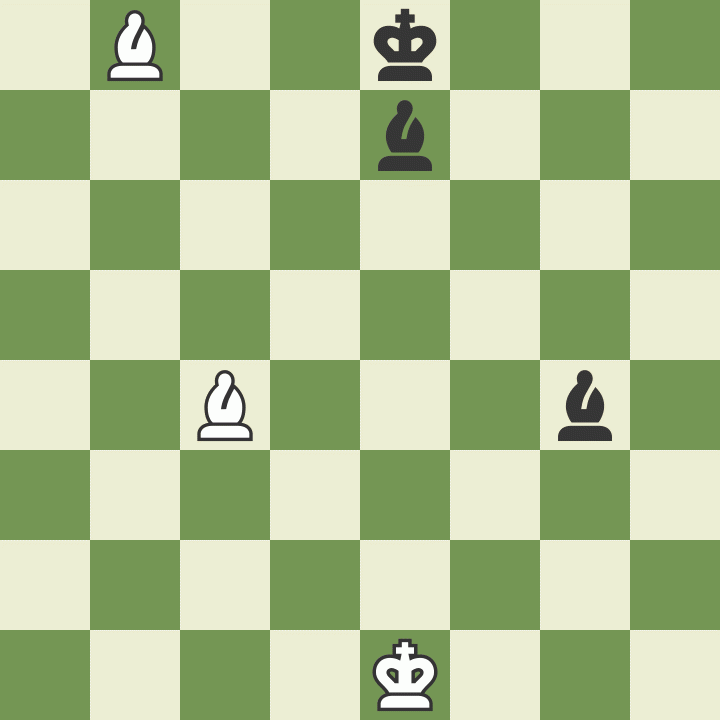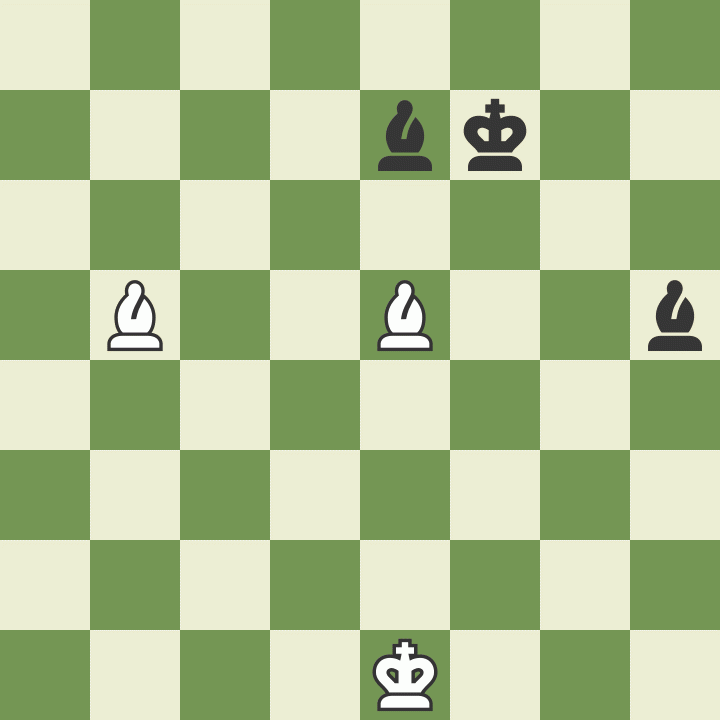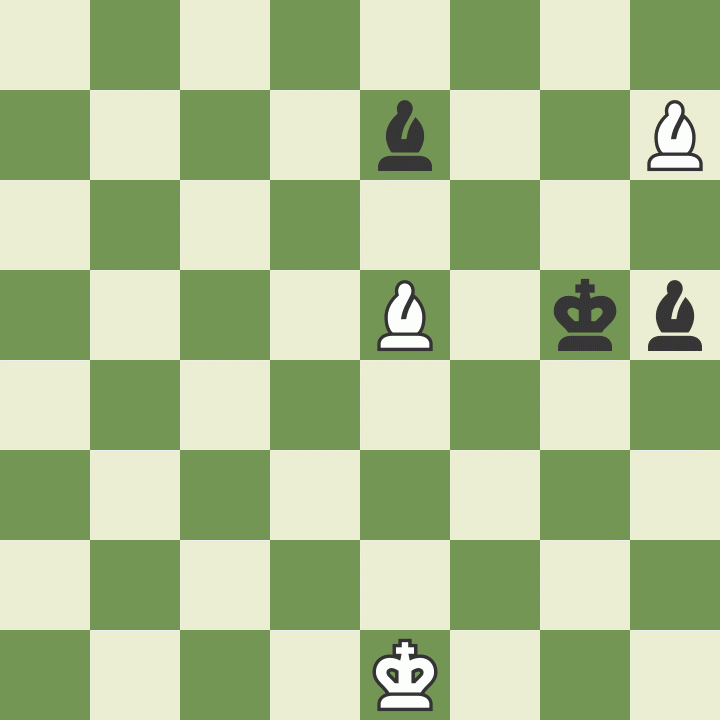
How to move a knight in chess
Knights move differently than other pieces - two squares in one direction and then one square at an angle of 90 degrees, the letter "G". The knight is the only piece that can jump over other pieces.
How to move a pawn in chess
A pawn is an unusual piece, it moves and captures in different ways: a pawn can only move forward, and capture only diagonally. A pawn can only move one square per move, except on the very first move, when it can move forward one or two squares. A pawn can only capture diagonally one square in front of it. A pawn cannot move or take back. If another piece is directly in front of the pawn, the pawn cannot move forward and cannot capture that piece.

Step 3: Learn the Special Rules of Chess
There are a few special rules in chess that may seem illogical at first. They were invented to make the game more fun and interesting.
How to promote a pawn in chess
The pawn has one remarkable feature - if it reaches the opposite side of the board, it can become any other piece (this is called "pawn promotion").

A pawn can be promoted to any piece. There is a misconception that a pawn can only promote to one of the previously captured pieces. This is wrong. As a rule, a pawn is promoted to a queen. Only pawns can transform into other pieces.

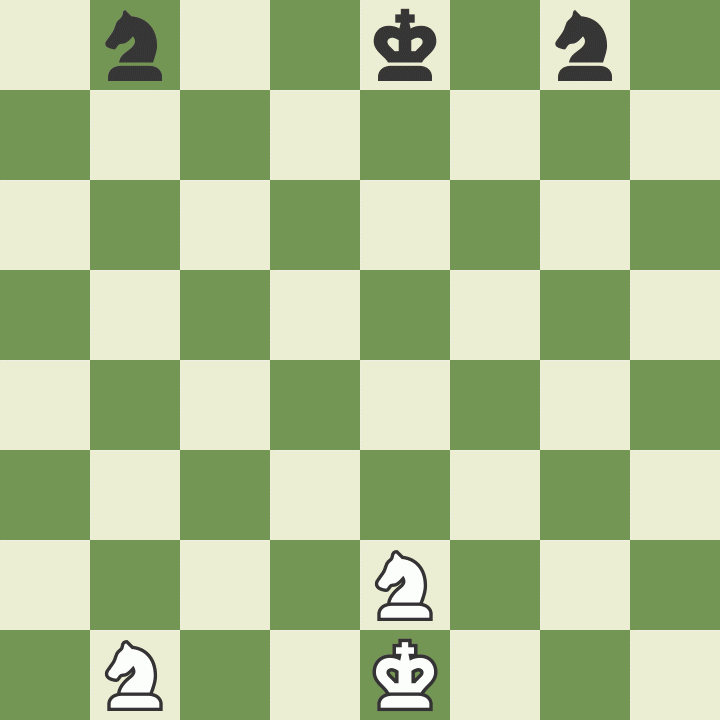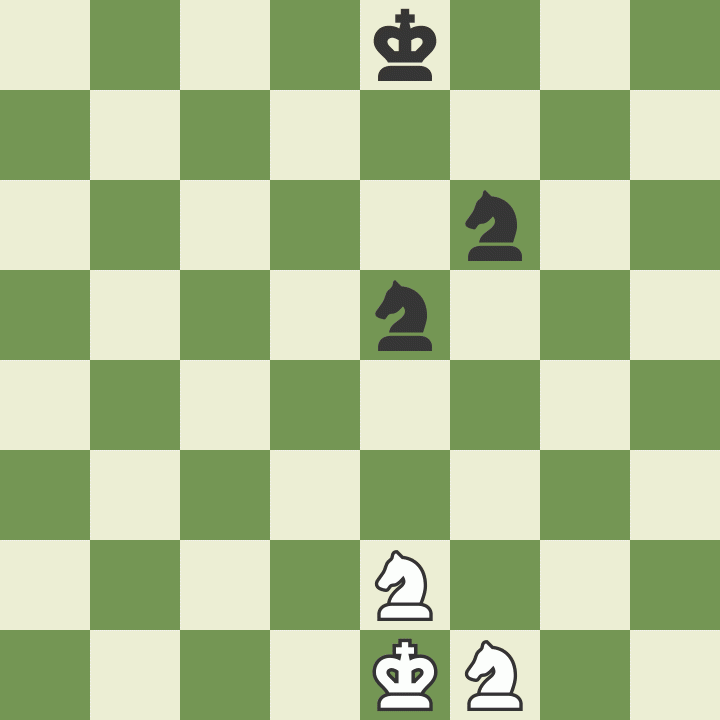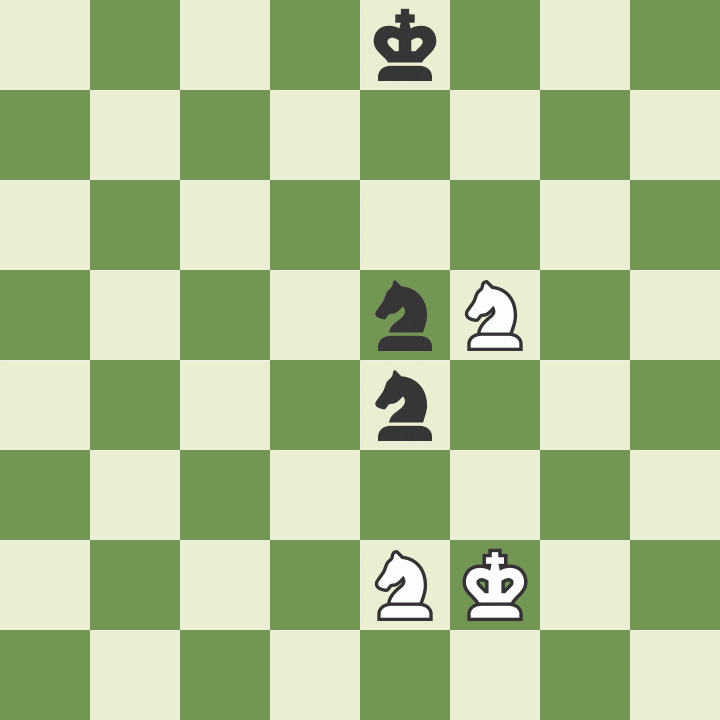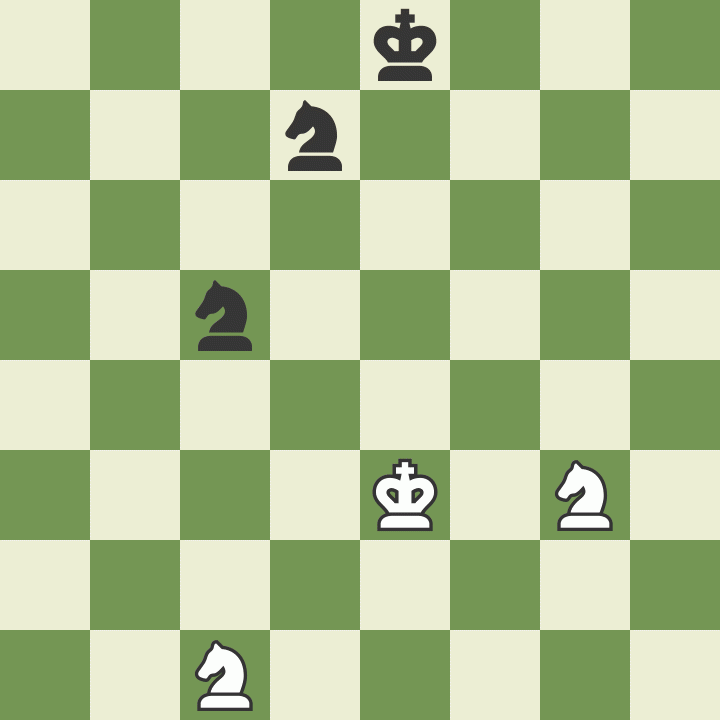
How to take on the pass
The last rule regarding pawns is called "". A pawn that has just advanced two squares in one move from its first starting position, can be captured by an opponent's pawn that occupies a square on the same rank and on an adjacent file, as if the last move of the captured pawn was only one square that it passed.

Such a capture is possible only on the move following the two-square advance, and is not possible afterwards. Study the example to better understand this unusual but important rule.

How to castling
Another special chess rule is called. Castling allows you to do two important things in one move: secure (if possible) your king and get your rook out of the corner, bringing it into play. When castling, a player moves his king two squares towards the rook, then that rook moves to the square the king just crossed (see example). Castling can only be done if the following conditions are met:
- before castling, the king never moved
- before castling, the corresponding rook never moved
- there must be no other pieces between the king and the rook
- the king cannot be in check or cross a square attacked by an opponent's piece
Please note that when castling to the kingside, the king is closer to the edge of the board. This move is called "castling short". Castling to the other flank, across the square where the queen was, is called "castling long". In both short and long castling, the king only moves two squares.

Step 4. Who goes first
The white chess player always moves first. To decide who will play white, chess players usually flip a coin or one of them guesses the color of the pawn hidden in the opponent's hand. Then white moves, then black, then again white, then black, and so on in turn until the end of the game. Being able to move first is a small advantage that gives White the opportunity to attack immediately.
Step 5. Recall how to win a game of chess
A game of chess can end in several ways: checkmate, draw, surrender, defeat by time...
How to checkmate in chess
The goal of the game is to checkmate the opponent's king. A checkmate occurs when the king is in check and cannot get away from it. There are three ways to defend against a check:
- retreat to another square (not castling!),
- block a check with another piece
- or take a piece that attacked the king.
If the king cannot avoid checkmate, the game is over. Usually the king is not taken or removed from the board, the game is simply declared over.

When the game ends in a draw
Sometimes a chess game ends not in a victory, but in a draw. There are 5 reasons why a game can end in a draw:
- " " appears on the board if the player who is to move has no possible moves and his king is not in check

When moving the queen to c7, Black is not in check, but he cannot make a move either. There is a stalemate on the board and the game ends in a draw.
- Players can simply agree to a draw and stop playing.
- There are not enough pieces on the board to checkmate (e.g. king and bishop against king).
- A player declares a draw if the same position on the board is repeated three times (not necessarily three times in a row).
- The last 50 moves were completed by each player with no pawn advances and no captures.
Step 6: Learn Basic Strategy Techniques
There are four simple things that every chess player should know:
Protect your king
Move your king to a corner of the board, where he is usually in less danger. Don't postpone castling. Generally, you should castle as early as possible. Remember, it doesn't matter how close you are to checkmating your opponent's king as long as your king is checkmated first!
Don't give away figures
Don't lose your pieces just like that! Each figure is valuable. You cannot win the game without pieces to checkmate. There is a simple system by which most players determine the relative value of each piece:
- Pawn - basic unit - 1 point
- Horse is worth 3 points
- Elephant is worth 3 points
- Rook is worth 5 points
- The queen is worth 9 points
- The king is priceless
These points do not affect the outcome of the game in any way - it is only a system that you can use to make decisions during the game. It helps you understand when it's best to capture an opponent's piece, exchange pieces, or make another move.

Control the center of the chessboard
You need to try to control the center of the board with your pieces and pawns. If you control the center, you will have more room to maneuver your pieces and make it harder for your opponent to find good squares for his pieces. In the example above, White, trying to control the squares in the center, makes strong moves, while Black makes weak ones.
Use all your shapes
In the example above, White has used all his pieces! Your pieces are useless as long as they are on the first rank. Try to develop all your pieces in such a way as to gather more strength to attack the enemy king. In a game with a worthy opponent, attacking the king with one or two pieces will not work.
Step 7 Practice Playing As Much as You Can
To improve in chess, the most important thing for you is to play! Whether you play at home with friends or family or online, you need to play a lot to get better. It's easy to find opponents online these days!
How to play chess variants
Although most people play chess by the standard rules, some people like to play chess with modified rules. They are called "variants of chess". Each option has its own rules.
- Chess-960: in chess-960 (Fischer chess) initial arrangement figures are chosen randomly. The pawns are placed as in regular chess, and the rest of the pieces behind them are placed randomly.
- king of the hill: in this variation of chess, you can achieve victory by occupying one of the squares in the center with your king chessboard, the so-called "top of the mountain."
- Swedish chess: This game is played in pairs. When one of the players takes an opponent's piece, it can be used by his partner. For example, if I play white and my partner, playing black, takes the white knight from his opponent, then by any of my future moves I can put him on any free square of the board.
- Crazyhouse: Very interesting game, where you can use the pieces taken from the opponent. For example, if I play white and capture a black pawn, it turns into a white pawn, which I can put on the board as my piece with any of my future moves.
- Up to three checks: In this game, the one who first gives three checks to the opponent's king wins.

Enjoy these amazing chess variations.
How to play chess-960
How to play by the rules of chess tournaments
Many tournaments use a set of common, similar rules. These rules do not apply to games played at home or online, but you may still want to use them.
- Touched - go- If a chess player touches his piece, he must make a move with this piece, if possible. If a chess player touches an opponent's piece, he must take it. A chess player who wants to touch a piece in order to correct it must first declare his intention by saying "correct".
- chess clock- Most tournaments use a chess clock, which allows you to set the time per game, not per move. Both opponents get the same time for the entire game and decide how to spend it on their own. Having made a move, the chess player presses a button or lever that starts the opponent's clock. If a player has run out of time and the opponent declares it, the player who made the delay loses the game (if the opponent has enough pieces to checkmate, otherwise a draw is awarded).
Frequently Asked Questions about Chess (FAQ)
This amount of information may surprise you a little. That is why we provide answers to the most frequently asked questions that are usually faced by people who are just starting their journey into the world of chess. We hope you find them useful!
How can I improve in chess?
Knowing the rules and fundamentals of strategy is only the beginning: chess is so complex that a lifetime is not enough to master everything! To improve, you need to do three things:
- play a lot- just keep playing! Play as often as possible. Learn from every game won or lost.
- Learn chess lessons- if you really want to make progress quickly, you should take a few lessons online. Here you can find .
- Enjoy- Don't be discouraged if you can't win all the games in a row. Everyone loses - even world champions. If you enjoy the game and know how to learn from losing games, you will love chess forever!
What is the strongest first move in chess?
Although there is no generally accepted strongest move in chess, it is important to fight for the center of the board from the very beginning. For this reason, most chess players make the first move of one of the central pawns (from the king or from the queen) two squares forward: 1. d4 or 1. e4. Others prefer 1. c4 or 1. Nf3. Most of the other moves are not so good. Bobby Fischer considered the best move for the king's pawn 1. e4.
Which color goes first?
The player with the white pieces always goes first.
Can a pawn move backwards?
The pawn cannot move backward. Reaching opposite edge board, it can turn into another piece (for example, a queen). The piece you've turned a pawn into can, of course, move backwards.
Is it possible to move more than one piece at a time?
During your turn, you can only move one piece, but there is one exception! When you castle, you move the king and rook in one move.
What is the most important piece in chess?
The king is the most important chess piece. If you lose the king, you lose the game. However, the most powerful chess piece is the queen.
When was chess invented?
The origin of chess is not completely known. According to the most common version, chess originated in India almost two thousand years ago from other similar games. Modern chess has been known since the 15th century, when the game became popular in Europe.
What was the longest game in the history of chess?
The longest tournament game (by number of moves) in the history of chess was played by Ivan Nikolic and Goran Arsović in Belgrade, Serbia in 1989.
What is chess notation?
The notation was invented so that it was possible to analyze the played chess games. Thanks to her, we have the opportunity to record all the moves of the game and play it as many times as we like. It is only necessary to correctly record your own moves and the moves of your opponent.

Chess notation will allow you to store all your games...
Each square has coordinates, and each piece is denoted by a capital letter (K - knight, C - bishop, Q - queen, L - rook and Kp - king).
What is the purpose of chess?
Chess is a game between two opponents on opposite sides of the board, lined with 64 squares of light and dark colors. Each player has 16 pieces: 1 king, 1 queen, 2 rooks, 2 bishops, 2 knights and 8 pawns.

A board, two chess players and 32 pieces is all you need to start a game.
The goal of the game is to checkmate the opponent's king. Checkmate is a situation where the king is threatened by an opponent's piece (the king is in check) and he cannot avoid this threat.
At first glance, it may seem that learning to play chess is quite easy, but in fact, this requires a lot of effort and remembering a few fundamental rules.
History of occurrence
People are still arguing about whether this game is a sport or an art. To date, computer technology has reached the point that any computer can easily solve "chess" problems of the highest complexity in a matter of seconds, but a person will need years of practice for this.
For the first time, the game in the form in which it is now customary to see it appeared 15 centuries ago in the East. Its rules were based on Arabic shatranj and Indian chaturanga. In the Middle Ages, the first chess tournament was held in Europe, in which only knights took part. These were real mind games. Chess in those days was considered the property of noble people.
There is one oriental legend according to which this game made a real rich man from a poor man. One wise man, who first showed the world how to play chess, asked for his “invention” one grain of wheat for one cell, two for the second, four for the next, and in a similar progression further to the end of the board. The ruler agreed, but he had no idea that in the end he would have to give 8.5 quintillion grains (a number with 18 zeros). As a result, several kilograms of wheat came out, which in those days was a great luxury.
As the legend shows, there are just so many variations in the development of events in chess, but there are isolated situations that develop on the board more often than others, and specialists study them. Great grandmasters know dozens of winning algorithms by heart, which are sought out and adjusted over the years in the course of hundreds of games.
Today this game has become popular all over the world. Many experts even recommend chess for children as a tool for developing deductive thinking.
Starting position
All pieces can only move on 64 squares of the board. Their correct location is also important. The board must be rotated so that there is a white square to the right of the player. On the plane itself there are 32 figures of two colors (black and white).

The rules of the game of chess state that each of the "armies" of opponents must be mirrored to each other. In the first rank, pawns are placed towards the enemy, and on the last line of the board, all the other pieces. Rooks are placed in the corners, then next to them are horses, behind them are bishops. In the center of the board, as expected, there are a queen and a king, and the second one must be on a cell of the opposite color.
Moves are made in turn, with White starting the game first. Often pawns go into battle at the beginning.
Pieces and their moves
The most important thing in chess is the king, but by itself he is practically helpless. Moves one cell in any direction. If you put him in a stalemate, then the game is lost regardless of the number of remaining pieces. This position is called mate, which means “to die” in Arabic.
The second most important figure is the most powerful weapon of the king, which can move along any straight line and pass an unlimited number of cells in one move.
The rook, along with the queen, is included in the group of "heavy" pieces. It can only move in a straight line to the sides, except diagonally. There is no limit on the number of cells passed per turn.
The bishop is closest to the king and queen. The variability of moves is limited by diagonals, but not by the number of cells.

The knight is the most unique and interesting piece on the board. Unlike the others, he only moves in a “G” pattern, that is, two squares forward in the chosen direction and one to the side. Before each move, the knight has 8 variations to maneuver.
There is another piece that is important to familiarize yourself with before playing chess - this is a pawn. And let her be considered the weakest on the board, but without her the king would be in danger of a very quick "death". It only moves forward 1 or 2 squares in its own half and one square in the other half.
You can capture an opponent's piece only if it is in the path of the player's move. Then its place is taken by a piece that beats it. If a situation arises when the king is threatened with deprivation of a place on the board, then it can be defended or a move can be made to the side. A pawn can capture any piece that is one square ahead of it diagonally.
Rules of conduct and cost of pieces
The king can fight anyone except the queen, as he can attack all the cells around him.
The cheapest and weakest of the pieces is the pawn. Its main advantage is the ability to make a fork, that is, to simultaneously threaten two elements of the enemy "army" at once.
The rook is equal in value to five pawns and stands above all except the queen. This is a very important figure for any strategy, with the help of which you can checkmate at any time.
An elephant and a horse are approximately equal in value, although they have different properties. Equivalent to three pawns. Of the shortcomings, it is worth highlighting the "dead zones" where these pieces cannot get (bishop - never, knight - for several moves).

The most useful and strong element on the board is the queen. Its cost is equal to two rooks at once. The queen is able to make not only a fork, but also threaten 8 pieces at the same time.
Before playing chess, it is important to familiarize yourself with one more nuance. If a pawn has reached the last opposite cell of the board (to the opponent's first line), then it can be exchanged for any piece that was previously captured by the opponent.
Game recording
A standard chessboard is a square and consists of 64 fields. Vertically, the numbers from "a" to "h" are always placed, and numbers from 1 to 8 are placed horizontally. It is these designations that are used in the notation of moves.
Thus, each cell has its own name, for example, d5, e1, f8, etc. In the record of the move of the figure, two fields (initial and final) are recorded separated by a hyphen. For example: a2 - a4.
In addition, the figures also have their own short designations - these are the first letters of their names (F, L, S, K). The only exception is the king. His abbreviation in the record - Kr. The pawn is not marked in any way.
Game outcomes
The rules of the game of chess describe only two possible developments of the final and one intermediate one.

An attack on the king is called a check. This action is indicated in the record with a “+” sign. Among chess players it is customary to call it an intermediate outcome, when there is a possibility of a checkmate. In the case of a check, there are several ways to defend: move the king to the side, cover it with another piece, or capture the attacker.
If the king has no way to get away from the attack, then the opponent has been checkmated. In this case, the game is considered won. Denoted by the sign "x".
A draw in chess is called a stalemate. This is a situation where the player has only one step left to checkmate, but it will not be possible to take it, because the opponent has no options for maneuvering any of the pieces. Denoted by the symbol "#".
Castling

The rules of the game allow the king and rook to be swapped once per game. Chess for children excludes the possibility of castling pieces, as it has some nuances that are quite difficult to perceive. A permutation is allowed only when neither the rook nor the king has made a single move and is not under attack by the opponent. Also, it cannot be done at the very beginning of the game. During castling, the rook stands close to the king, and he stands on the adjacent square on the other side.
Russian chess
The rules of this game are no different from its Arabic counterpart. Russian chess is a board with 64 squares and 32 pieces. The pawns here are called tavrels. The rest of the figures have names: prince, rider and warrior. The king is a sorcerer.
How to play chess with such pieces? The main difference is the tower position. During the game, not a single piece is removed from the board. If one of them beats the other, then it is placed on top of the first, forming a kind of tower, and so on.
The game continues until the first figure appears on the sorcerer.
A chess game is played on a board consisting of 64 squares, alternately light (white squares) and dark (black squares). Rows of fields are called lines, which can be verticals, horizontals and diagonals.
Each horizontal line is numbered from 1 to 8. Each vertical line is numbered in Latin letters from "A" to "H". Each field of the board has its own coordinates, which are formed by writing the name of the vertical and the number of the horizontal.
The board during the game is positioned so that each partner has a white corner field on the right. If this requirement is violated, the resulting position is considered impossible. The game should be interrupted. The position of the board is corrected. Then the created position is transferred to it. After that, the party continues.
Pieces move around the chess board. Look and remember, in order to learn how to play, you need to know how the pieces are placed before the start of the game. In the first row there are pawns, behind them are pieces: the extreme ones are rooks, followed by horses, then bishops, in the middle are the king and queen. The queen always stands on her color: white - on a white field, black - on a black one. Chess is always played by two people. One plays with white pieces, the other with black pieces. You can move one piece per move. The players take turns.
We begin to get acquainted with chess pieces, and learn to walk with them:

King. The most important figure, but very weak. If the king dies, the game is lost. The king moves to any field adjacent to him for only one maple. The main goal of the game is to put the opponent's king in a hopeless situation, to declare checkmate to him. If you managed to declare checkmate, you won and the game is over.

Queen. The strongest figure. People call her the queen. She walks as she likes: horizontally, vertically, and diagonally, forward and backward. In one move, the queen can pass both one cell and the entire chess field.

Rook. She moves almost exactly like a queen, only she can't move diagonally.

Pawn. The weakest figure. It moves only forward, and only one square, only once from the starting position a pawn can make a double move (through a square, for example c2 - c4). However, if the pawn manages to go through the entire field, then reaching the last row, it can turn into any chess piece, except for the king. Isn't it a bit like a fairy tale about Cinderella, who turns into a princess?

Horse. This is a very interesting figure. The knight walks as follows: two cells forward, one sideways, or two cells sideways, one forward (people say the letter G).

Elephant. This piece only moves diagonally, forward and backward. The elephant moves only in the cells of its own color.

You know that only one piece can be moved in one move, but during the game, each player is allowed to make a double move once - to move the king and rook at the same time. This move is called "castling". Castling is done as follows: the rook must be moved to the king, the king jumps over it and stands on the other side. You cannot castling if: the king and rook have already made a move; the king is in check; after castling, the king and rook must not remain under attack.

 This only applies to pawns. It is possible to capture a pawn on the aisle when it makes a double move. Once the opponent's pawn has made a double move, you can remove it from the board by placing your pawn on the square as if the opponent's pawn had made a simple move. You can capture a pawn on the aisle only immediately after a double pawn move. Did not take it right away - the opportunity disappears. Look at an example.
This only applies to pawns. It is possible to capture a pawn on the aisle when it makes a double move. Once the opponent's pawn has made a double move, you can remove it from the board by placing your pawn on the square as if the opponent's pawn had made a simple move. You can capture a pawn on the aisle only immediately after a double pawn move. Did not take it right away - the opportunity disappears. Look at an example.
To an ignorant person chess rules may seem simple enough, but in practice the situation is different.
To begin with, it is worth saying that chess is a game involving two people. The pieces they move with are located on different sides of the board, which contains 64 black and white fields.
Different figures alternately move along 64 squares of the board. The game begins with the correct installation of the board. It is necessary that each of the players have a white square in the lower right corner, respectively, black on the left.
The chessboard is marked horizontally with letters from a to h, in the vertical direction - with numbers from 1 to 8. It is with their help that the current game is recorded.
Because the article is quite large - we made it easy to navigate.
Article navigation:
The meaning of the game of chess
Arrangement of pieces in chess
If you do not know how to arrange chess on the board, then read this paragraph. Opponents play on opposite sides of the board, one of them moves with white pieces, the second with black pieces. The pieces in each game are placed in the same way as follows:
- Lines number 2 and 7 are pawns;
- The corners of the board are rooks;
- Next to the rooks are horses;
- Next to the horses are elephants;
- In the middle - a queen (should stand on a cell of the same color as it: white - on white, black - on black);
- Next to the queen is the king.
The first move in the game goes to the player with white pieces (the decision on who plays which pieces is made by lot). So, first the white pieces move, then the black ones, then again the white ones, then the black ones, and so on.
In the image below you can see how to correctly arrange the chess pieces.

How chess pieces move
The most significant and significant chess piece is the king. Possible moves of the piece: diagonally, horizontally, vertically to the adjacent field. The king does not have the right to make moves to an adjacent field if it is attacked by one of the opponent's pieces, or if another piece of the same color as the king is on this field.
The queen is the most powerful piece in chess. Its conditional value is 8 pawns. It combines the strength of both the rook and the bishop, as it can move vertically, diagonally and vertically (if there are no other pieces on the way).
The rook has the right to make moves in the vertical and horizontal direction, if there are no other pieces on its way. The conditional value of a rook is 5 pawns.
The bishop can move diagonally to any square, as long as there are no other pieces there. There are black-sexed and white-skinned elephants (the first ones walk through the black fields, the second - white ones).
Knight - conditional value - 3 pawns. Possible year - in the form of the letter "G". This means that at the beginning of the turn, it can move two spaces in the vertical direction, after which it can move one space in the horizontal direction. It is also possible for the knight to move - one square in the vertical direction and two - in the lateral horizontal direction. The knight piece has the right to "jump" over other pieces.
Pawns have the right to move in the vertical direction, but they can also attack diagonally and take the place of the piece that was beaten. In a situation where the pawn is in its original position, it can move through one square or move only to the next square forward. In the case when she is already in the game (that is, she made moves), then she can only move one square forward.
Turning and taking on the pass
A distinctive feature of pawns is that they have the right to become other pieces (except the king). To do this, the pawn must reach the last line of the board (the first one for black and the eighth one for white). The choice of a piece is carried out by the player who makes the move. As a rule, a pawn is promoted to a queen.
Also, a pawn can capture on the aisle, that is, capture another player's pawn piece, which was moved simultaneously to two cells of the board.
Castling in chess
Castling occupies a special place among all the rules of the game of chess. How to castling in chess is described below. This move makes it possible at the same time from the corner of the chessboard to take a more advantageous position, as well as to secure the king. The essence of castling is that the king piece changes position towards its rook by two squares, after which the rook moves to the adjacent square on the other side of the king piece. However, long castling in chess cannot be done just like that, for this a number of important conditions must be observed:
- The king moves for the first time in the current game;
- The moved rook moves for the first time in this game;
- There are no other pieces on the squares between the pieces of the king and the rook, they are free;
- The king is not in a check situation, and the squares he is about to occupy or cross must not be occupied and attacked by enemy pieces.
Below is a picture that will show you how to castling correctly. The picture is indicated.

Chess: rules of the game. Checkmate
At the beginning of the article it was said that the main goal chess game is to checkmate the opponent's king. To do this, the king must get into check, but he can get out of it using one of three ways:
- Ensure safety by moving to another square of the board (castling is not allowed in this case);
- To take a piece himself, with the help of which the opponent is going to check (if possible);
- Defend against an attacking piece with another, with your own piece.
If it is impossible to avoid checkmate, the game comes to an end. In this case, the king remains on the board, but the game is considered over.
Also, if you want to learn how to play chess, learn the basic rules, you need to know when a draw is declared. There are 5 rules:
- If a player should move next, but cannot do so due to the position of the pieces;
- Consent from both players;
- The lack of a sufficient number of pieces on the board, allowing you to checkmate the opponent;
- 50 consecutive moves were made, however, none of the opponents made , as well as capturing a pawn or piece of the opponent;
- The player can declare a draw in the event that there was a three-time repetition of identical positions.
Blitz chess rules
Blitz chess is a chess game in which both players are given 5 minutes for each move. The rules for the game are the same as for ordinary chess, the only difference is that all moves must be made very quickly.
In this case, the players require utmost attention, composure. The most important rule is that the moves must be made very quickly, most of the time may be required at the beginning of the game, so it is recommended to practice a lot and learn well all the possible variations of the different stages of the chess game.
It is also not bad if you learn, by playing ordinary chess, to put different kinds checkmates, in a short time to carry out a quick size of pieces in order to gain an advantage over the enemy.
Having familiarized yourself with the rules described above, you can already try to play the first game of chess. However, in order to learn how to play really well, it takes time, long trainings, training, studying various positions, moves, nuances of games and, of course, constant practice.
Chess is a game for two. One player (White) uses white pieces, and the second player (Black) usually plays black pieces. The board is divided into 64 small black and white squares (fields).
There is a system (notation) that describes the situation on the board and the movement of all pieces and pawns.
EXAMPLE 1
EXAMPLE 2
In this system, the vertical rows of fields are called lines (verticals) and are denoted by Latin letters: a, b, c, d, e, f, g and h. Horizontal rows of fields are called rows (horizontals) and are numbered from 1 to 8 (1st row, 2nd row, etc.). Each field has its own designation (for example, the field e4, marked with a yellow circle on the board).
EXAMPLE 3
Oblique rows of fields - diagonals are indicated by end fields, for example: a2-g8 And h4-d8 diagonals (marked with red lines). While verticals and horizontals include margins different color, then the diagonals consist of fields of the same color, either white or black fields. For example, the diagonal b1-h7 white-field (marked with a green line), and the diagonals c1-a3 And a3-f8 black-field (marked with a blue line). 2 diagonals consisting of 8 fields ( a1-h8 And h1-a8) are called long (main) diagonals (marked with yellow lines).
EXAMPLE 4
STARTING POSITION
At the beginning of the game, each side has:
Pawns and pieces (together) are called material. At the beginning of the game, the parties have material equality. The goal of the game is to capture the opponent's king. This is called checkmate the king.
The queen and rooks are heavy pieces. Elephants and horses are light figures.
Chess pieces in the notation are described as follows: king - Kr; queen - F; rook - L; elephant - C; horse - K; pawn - p.
In the chess notation of a game, the pawn designation (p) is most often omitted.
Arrangement of pieces and pawns in this moment a position or situation is called on the board. The diagram shows the starting position.
White occupies the first and second ranks, black - the seventh and eighth. The board must be positioned so that the top left corner box is white ( h1 for whites and a8 for blacks). In the initial position, the white queen must be on a white square ( d1) and the black queen - on the black field ( d8).
EXAMPLE 5
The left half of the chessboard (from a to d) is called the queenside, and the right half of the board (from e to h) is called the kingside.
EXAMPLE 6
Four central fields ( d4, d5, e4, e5) are called 2 center. This is a very important part of the board.
MOVE
Any movement of a piece or pawn on the board is called a move. Players make moves in turn, playing white starts first.
You cannot move a piece onto a square already occupied by your own piece or pawn. The knight is the only piece that can jump over squares occupied by its own pieces or pawns and enemy pieces.
Rook
The rook can move any number of squares either horizontally or vertically.
In the diagram, the white rook can go to any square on the e-file or to any square on the 4th rank, for a total of 14 squares.
EXAMPLE 7
Elephant
The bishop can move any number of squares along the diagonal.
In the diagram, the white bishop on d4 can go to any square on the diagonals a1-h8 And g1-a7, in total 13 fields are available to him. The other white bishop has only 7 squares at his disposal.
In the starting position, each player has one bishop that can only move on white squares and one bishop that can only move on black squares. They are often called light-squared and dark-squared elephants.
EXAMPLE 8
Queen
The queen can move any number of squares vertically, horizontally and diagonally, as shown in the diagram.
Thus, the queen combines the capabilities of the rook and the bishop, in addition, it can move along both the white and black diagonals. The diagram shows that the queen standing on d4, 27 fields are available. Such mobility makes the queen by far the strongest piece.
EXAMPLE 9
Horse
The horse moves in a very unusual way.
From the black field e5 the white knight can go to one of the 8 white squares, as indicated by the arrows. The knight moves 1 square forward and one diagonally, and only on the field of the opposite color to the field on which it is located at the beginning of the move. The diagram shows that the knight jumps over the field d5 and gets on the field c6 or c4; through e6 on the field d7 or f7; through f5 on the field g6 or g4, and through e4 on d3 or f3. The knight always moves from white to black and vice versa. We can say that the horse walks with the letter "G".
EXAMPLE 10
This is the only piece that can jump over its own and other people's pieces.
Although the white knight is surrounded on all sides by its own and other pieces and pawns, this does not prevent it from moving to the fields marked with markers.
The horse stands out for its exceptional maneuverability.
The well-known problem is to go around the whole board with a knight, having visited each square only once. Mathematicians have established that there are more than 30 million such routes. Although the best minds have been solving this problem for several centuries, no one has established the exact number of such routes.
EXAMPLE 11
King
The king can move one square in any direction (diagonal, vertical, horizontal).
On the diagram, the squares to which the king can move are marked with dots.
In the corner of the board, the king's mobility is reduced: on the extreme rank, only 5 squares are available to him. When the king is located on the corner square of the board, then only 3 squares are available to him.
EXAMPLE 12
TAKE
A piece can capture an enemy piece or a pawn in its path. This piece is removed from the board and its place is taken by a piece that makes a move. After that, the move is considered completed. A piece can capture an enemy piece or pawn only if it can move to the square where the capturing piece is located.
White's move. The white queen threatens the black rook and bishop at the same time and can capture one of these pieces. Since the rook is a more valuable piece, White takes the rook on d4. The following position appears:
EXAMPLE 13
Before taking.
1. Јd4 After taking:
The player is not required to make a possible capture.
Pawns
To denote a pawn, we will add the file on which it is located or the square: the f-pawn, the g4-pawn, and so on. Pawns are also named after the piece located on this file in the initial position: the queen's pawn (d-pawn), the king's pawn (e-pawn), the rook's pawn (a or h pawn), the knight's pawn (b or g), the bishop's pawn (c or f).
Unlike pieces, which can move in any direction, a pawn can only move one square forward vertically. An exception for the initial position, for example, a white pawn on the second rank and a black pawn on the 7th rank can move 2 squares forward at once.
Pawns move only vertically, but captures are made diagonally, to the left or right.
In the diagrams, white pawns can only move up and black pawns can only move down.
Let's look at the pawn moves in the diagram. The white pawn on a4 can only move to one square:
EXAMPLE 14
[Since the white pawn c2 in the initial position, then she can also play 1. c3;
The white pawn on d4 does not threaten the black king, but can take one of two black pieces: 1. dc;
Black can make the following pawn moves: 1... ab
In addition to the usual capture, a pawn can capture an opponent's pawn (but not a piece) on the pass.
The situation (example 15) occurs after the moves
1. e4 e6 2. d4 d5 3. e5 f6
A similar situation can arise if Black plays 3...f5 instead of 3...f6
EXAMPLE 15
Now White has the right to take the black f-pawn on the pass with his e-pawn. To do this, White removes the black pawn from the board and moves his pawn to f6. In notation: 4. ef
However, if White does not immediately use the right to capture on the aisle, then on the next move he already loses it. If in Diagram 1 White does not play 4. exf6, then on the next move he can no longer capture this pawn. Only the white pawn on the fifth rank and the black pawn on the fourth rank can receive the right to capture on the aisle.
The mobility of the pawn and its attacking potential is much lower than that of any piece (the rook pawns control only one square, while the remaining pawns control two squares). However, a pawn can be promoted to any piece except the king. When a pawn reaches the last row (white pawn - 8th row, and black pawn - 1st row) it can promote to a piece (queen, bishop, rook or knight) of the same color, regardless of whether there are already such pieces on the board or not. This is called pawn promotion.
Thanks to this ability of the pawn, the player can have more pieces of a certain type than in the initial position, several queens, for example. Most often, the pawn turns into the most powerful piece - the queen.
When the pawn reaches the last rank, the notation after the pawn's move indicates the piece into which the pawn advances. In position on the diagram, the notation would look like this:
EXAMPLE 16
1.d8 Ј - this means that the white pawn has reached the 8th rank and has become a queen.
A pawn can also promote to a queen by capturing the bishop on e8: 1. de Ј ;
White can promote his pawn to any other piece. In this case, for example, it is best to take the bishop and turn the pawn into a knight, which immediately attacks the black king and queen at the same time 1. de ¤
NOTATION
In this position, White moves the knight from e3 to c4, simultaneously attacking the black rook on b6 and the pawn on d6. Such an attack is called a double strike. Black removes the rook on b8 and White wins the d6-pawn.
Now Black faces a new danger: White threatens the bishop on c6. To avoid the threat, Black takes him to d7. Let's display these moves using chess notation. White's first move
EXAMPLE 17
1. ¤ c4 , where 1 is the move number, K is the abbreviation for the piece making the move, and c4 is the square the piece moved to. White's next move and Black's response are described in the notation in the same manner. The symbol is used to indicate a capture. x(multiplication sign), for example 2. TO xd6. Now we can list all the moves in this example: 1... ¦b8 2. ¤d6 Ґd7 The three dots before the move (when necessary) indicate that it is Black's move.





